- Undercarriage:
Tracks/Crawler: Provide mobility and stability on uneven terrain.
Track Frame: Supports the weight of the excavator and houses the drive mechanism.
Drive Sprockets: Power the tracks.
Rollers: Support the track and provide a smooth surface for movement.

- Upperstructure:
Cab: Operator’s compartment with controls and instrumentation.
Engine: Provides power to the hydraulic system and other components.
Hydraulic System: Uses fluid pressure to power the excavator’s movements.
Swing Bearing: Allows the upperstructure to rotate relative to the undercarriage.
- Boom, Arm, and Bucket:
Boom: The main arm of the excavator, providing reach and elevation.
Arm (or Stick): Connects to the boom and provides further reach and digging force.
Bucket: The digging tool attached to the arm, available in various shapes and sizes for different tasks.
- Hydraulic Components:
Hydraulic Pump: Generates hydraulic pressure.
Hydraulic Valves: Control the flow of hydraulic fluid to different actuators.
Hydraulic Cylinders: Convert hydraulic pressure into mechanical force to move the boom, arm, and bucket.
- Other Components:
Counterweight: Balances the weight of the boom and arm.
Fuel Tank: Stores fuel for the engine.
Electrical System: Provides power to lights, gauges, and other electrical components.
Please note that this is a simplified overview, and the specific parts and their configurations can vary significantly depending on the make, model, and size of the excavator.
If you can provide a more technical image or specify the type of excavator you are interested in, I may be able to provide a more detailed diagram.
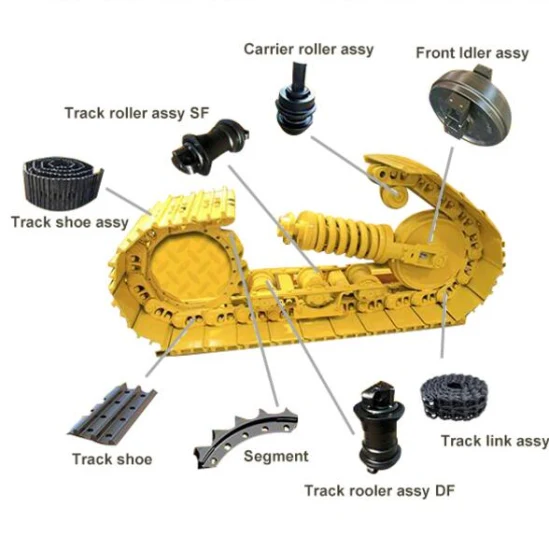
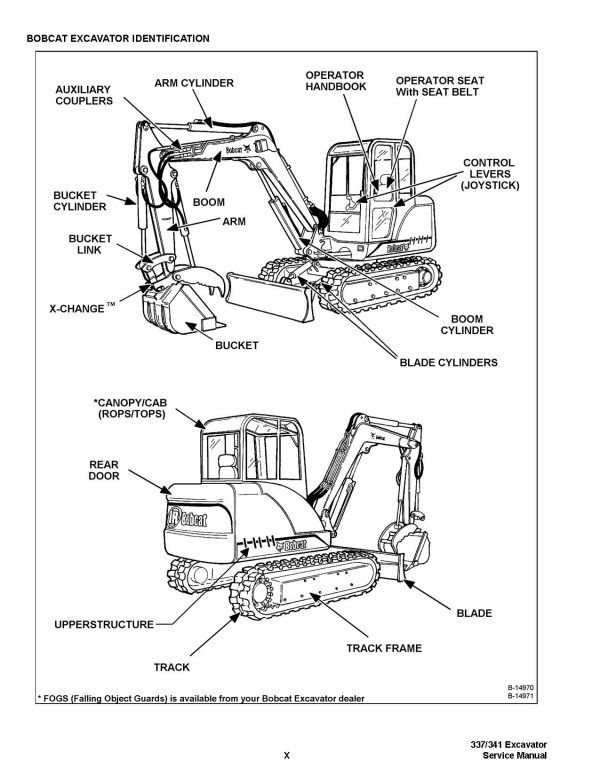
Image 1 showsexcavator parts diagram:
Boom: The main arm of the excavator.
Stick/Dipper: The arm connected to the boom that holds the attachment.
Bucket: The digging tool at the end of the stick.
Tracks: The metal treads that the excavator moves on.
Cab: The enclosed area where the operator sits.
Image 2 showsexcavator parts diagram:
A side view of the excavator: This view shows the relationship between the boom, stick, bucket, and tracks.
A cutaway view of the undercarriage: This view shows the tracks, sprockets, and some internal components.
Engine: The power source of the excavator.
Hydraulic system: The system of pumps, valves, and cylinders that power the excavator’s movements.
Swing gear: The mechanism that allows the excavator’s upper body to rotate.
Detailed labeling of individual parts: A true parts diagram would label every component with a specific name or number.
In summary: These images provide a general overview of an excavator’s structure but are not detailed enough to be considered technical parts diagrams.